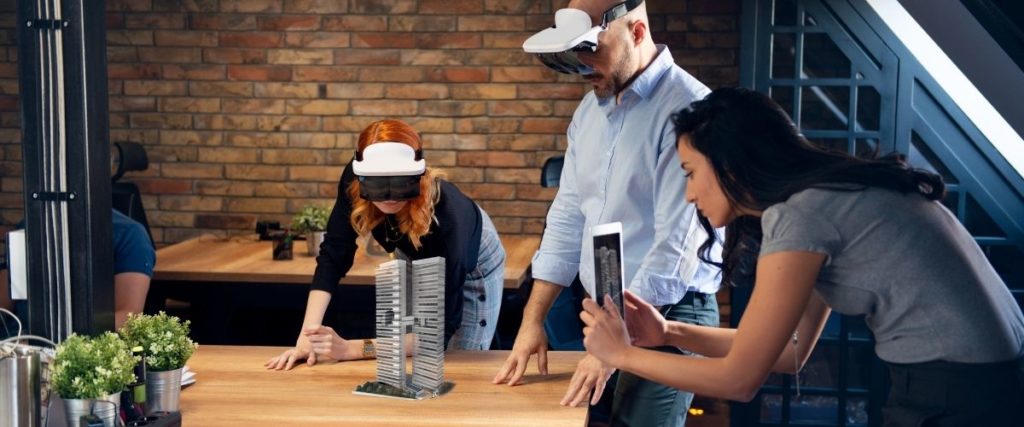
Augmented Reality (AR) is a newly developed technology expanding to not just the entertainment industry but in education, health, and construction sectors. Find out 6 ways the Augmented Reality industry is reinventing these sectors.
Augmented Reality (AR) integrates a computer-generated feature into the real world and enhances the physical world through the use of digital technology, such as visual stimuli or sound elements. In 2016, 500 million individuals ventured out of their homes, mindlessly swiping and walking as directed by their phones, trying to “catch” Pokémon. Pokémon GO has become one of the most downloaded AR apps since 2016- using a GPS (Global Positioning System) to insert Pokémon into the “real world”, users can catch Pokémon on the way to- or even at-work. The AR technology industry has since expanded to social media platforms like Snapchat and Instagram, where users are able to put heart eyes, rainbows, and even dog-ear filters on their heads. The AR market will soon rise up to US$25 billion by 2025, with consumers spending US$6.3 billion on AR devices alone. Since AR is cost-friendly, accessible, and effective, as no equipment is needed besides a smartphone, more industries are starting to implement this technology on their platforms. Here are 6 sectors the augmented reality industry is reshaping.

1. Education
AR enhances students’ learning capacity and skills like problem-solving, spatial awareness, and teamwork by providing an additional tool to the classroom. AR is a great way to gain higher student engagement, making learning fun and interesting. Assemblr EDU is an app developed in Indonesia to help teachers make interactive lesson plans. In the app, there are a dozen free lesson plans and modules to help students stay more focused during class. Assemblr EDU allows teachers to create a virtual zoo so that students can “meet” prehistoric animals while in the classroom.
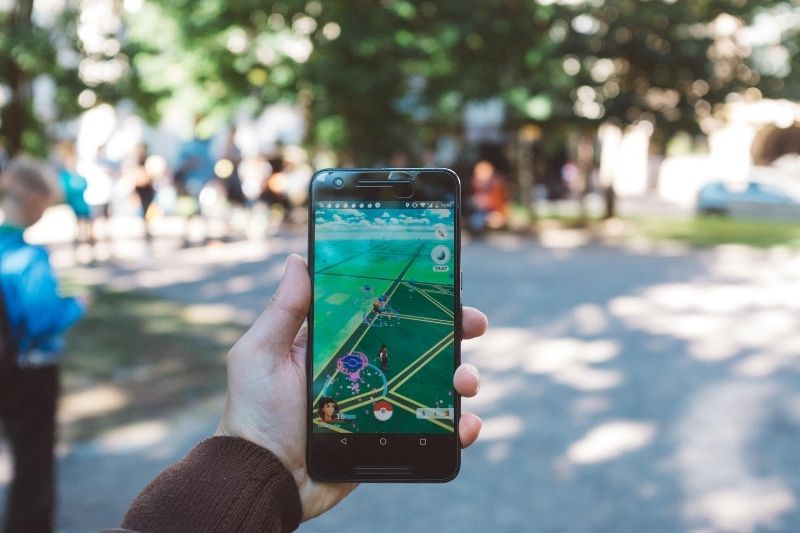
2. Tourism
A new study shows that 50% of travellers would use AR tours to get inspiration for their holidays. AR apps like Pokémon GO rely on a GPS to track which location users are in. Developers are planning to create other location-based apps for city tours and navigation, with restaurant recommendations, activities, or even fun facts about destinations popping up as users visit them. Museums will benefit greatly from AR, and one of its many possible uses is adding explanations, information, history, and fun facts on any given object or exhibit, upon scanning a QR code, for example.
The AR industry will continue to bloom in museums to enhance the visitor’s experience and generate more business, developing more interactive exhibits, and reinventing museums as we know them. Japan’s TeamLab is the world’s first digital art museum and one of the best examples of AR integration. Using 520 computers and 470 projections to add a third-dimension to displays, bringing objects or scenes to life, visitors can make a cartoon from a picture jump from frame to frame, use an app to create animals and plants, and even “communicate” with a Japanese anime monster.
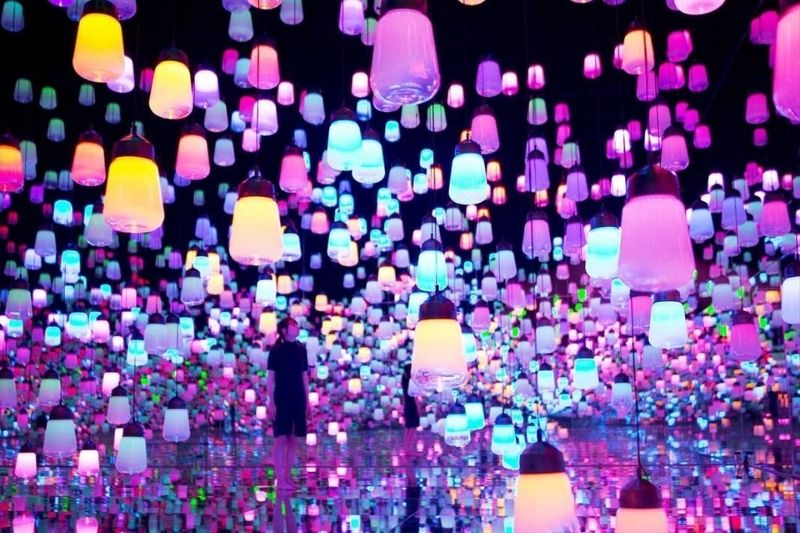

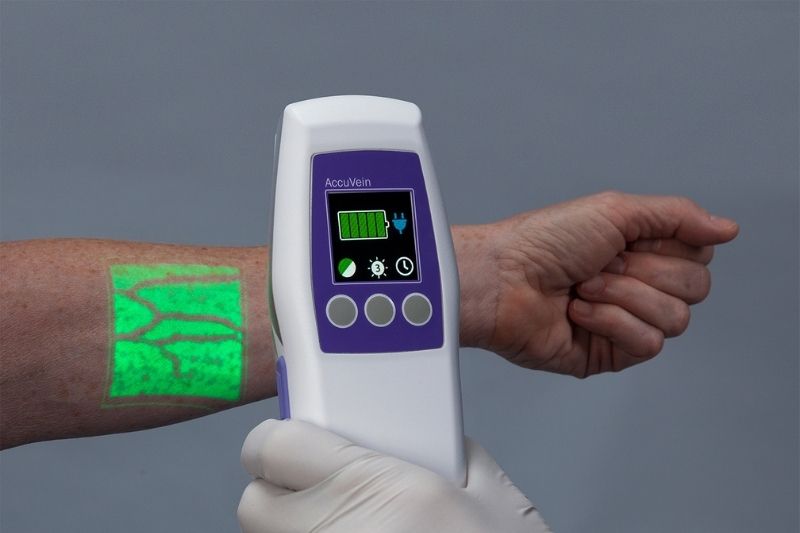
3. Healthcare
The Asia-Pacific AR healthcare market size is expected to grow 22.1%, predicting a revenue of $349 million by the end of 2026. Google recently partnered up with BioDigital to develop an AR technology where medical students can learn about the human body systems through a life-size view. Holoeyes is a Tokyo MR service (a mixture of virtual and augmented reality) that scans CT data and uploads it onto a 3D imaging system called Holoeyes XR for teaching, training, and surgery guidance. AccuVein is a US-based company that uses AR technology to guide nurses to the right vein when starting an IV drip, injection, or conducting a cosmetic procedure. The company uses an infrared laser on the patient’s skin which produces dark lines where veins are located. This product is available to purchase from over 130 distributors worldwide.
Looking at current HealthTech trends, companies will be integrating more and more AR into their products. We might see inventions where users can scan pharmaceutical drug packages to get information and also place an order online. Or even being able to receive consultations from doctors digitally, with them standing in the middle of your living room.
4. Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) makes construction professionals’ lives easier as they are able to plan, design, and construct buildings efficiently. Combined with AR, the construction industry will reach a whole new level of enhancements. With 3D models, designers can evaluate designs in a more immersive way, experiencing and interacting with their design from different perspectives. It also enables construction workers to visualise where doors should be placed, and where walls should meet. AR can also be used for training purposes, as students can practice looking for flaws, holes, and cracks in a “building” to ensure it is following safety regulations. iStaging is a Taiwanese company focused on using AR and VR technology to help interior designers see which furniture or design fits the interior of a house, just by using their smartphone camera. The app can also help realtors conduct virtual tours.
5. Retail
With everything moving online, especially since the Covid-19 pandemic, shopping malls have to use creative ways to attract more customers. IFC mall in Hong Kong celebrated Christmas by installing an interactive AR element where visitors can use their smartphone cameras to scan a QR code to add snowmen, Christmas trees, and other festive decorations virtually around the mall. DRNK AR is a Singapore based company launched by Omniaz for wine, beer, and spirits: consumers can scan a beverage and are given information about the product’s nutrition value, aromas, and other information. Users can also purchase products directly from the app. As online shopping increases, the number of returns also increases, and it is estimated that 30% of all products will be returned. Innovators are creating 3D visualisations to give shoppers the opportunity to see how the products look on themselves before purchasing. China’s selfie app, Meitu allows users to try on different makeup looks and colours to decrease the amount of cosmetic product returns.
6. Marketing
AR has provided a unique way for companies to sell their products and brand. Many startups, organisations, and entrepreneurs are investing in AR technology because it helps to create a lasting user experience, increases clientele engagement, and also promotes brand loyalty. Hong Kong-based Intermed Asia is a company that creates creative eye-catching products that utilise AR. Most of their products involve making interactive company cubes that showcase their company’s background, logo, and other promotional features like calendars. Their magic concept product line involves using your smartphone to display your company’s 3D logo, video, or selfie. Starbucks Shanghai also recently launched an AR customer experience feature where they can scan a QR code to follow the journey of a coffee bean, which generates a strong and memorable brand impression.
Although the AR gaming industry is still driving the increase in market sales, it is not the only field where this technology can be applied. The AR industry will continue to expand in other sectors as well, creating more engaging content and interactive experiences, which will increase user bases and redefine these sectors, paving the way for a fully technologically integrated future.

Related Articles
A New Virtual and Augmented Reality for Learning
Sandbox VR: How a Millennial Founder Engineered a USD 79M Gaming Sensation





