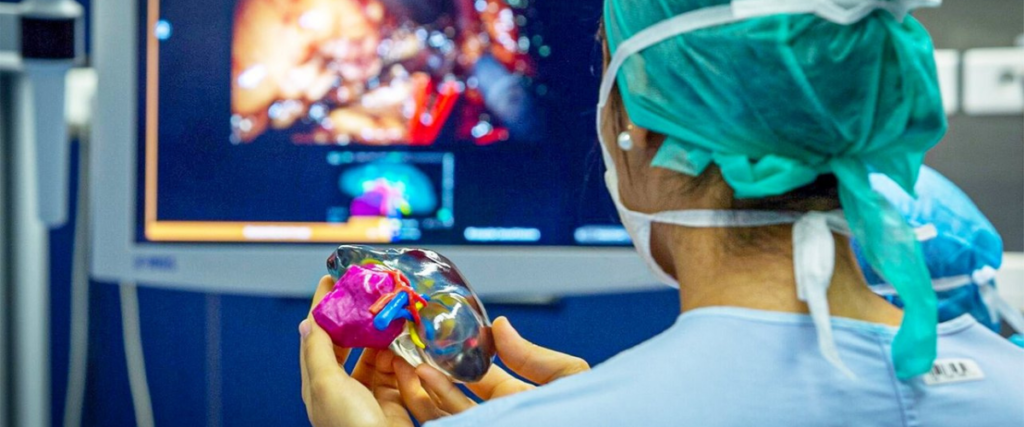
From architectural models to artificial human organs, 3D printing technology can produce or replicate tangible objects with specific functions. With more 3D printers now being available on the market, companies and individuals are considering adopting this breakthrough technology. Read on to learn about the potential applications of and trend forecast for 3D printing technology.
3D printing technology is expected to play a crucial role as a tech trend in the coming years. With the potential to produce any prototype and even manufacture objects for practical use, the industrial demand for 3D printers is rising at a global level. The ongoing pandemic has also contributed to the push for the accessibility of 3D printing technology, as people seek personalised equipment and a more efficient supply chain, a solution 3D printers can offer.
While 3D printing technology is well known for its common purpose of producing simple prototypes in industrial domains such as car manufacturing or architecture, there are now 3D printers that are even capable of creating artificial human organs for medical necessities. These new technological innovations have the potential to influence any industry, and could disrupt traditional production and manufacturing processes.
Into 3D Printing
While conventional printers are designed to print two-dimensional graphics on pieces of paper, 3D printing produces a three-dimensional object from its digital model by adding layers of thin material on top of each other. Hence, the outcome would be a tangible object.
Once a 3D digital model is created through a software programme of the user’s choice, it will be divided into slices of thin layers of material for the 3D printer to read. The printer will then receive this file and print the design by layering the appropriate material.
Materials may vary depending on the type of the printer or the final object. Common ones include functional plastics, metals, ceramics, and sand. Research is being conducted on the use of biomaterials to even produce edible objects through 3D printing technology.

Applications
Although 3D printing is commonly used for the creation of prototype designs, recent developments have expanded its possible applications, inviting many different industries to adopt and invest in this technology.
Organ Bioprinting
One of the notable sectors 3D printing is disrupting is the medical field. With the global shortage of organs for patients in need, the development and distribution of three-dimensional organ bioprinting will be a breakthrough in the coming years. By utilising 3D printing technology, cells can be assembled along with other biomaterials in layers to produce artificial organs. Cyfuse, a Japan-based startup, is currently working on a 3D printer that would be capable of producing 3D cellular products for practical use.
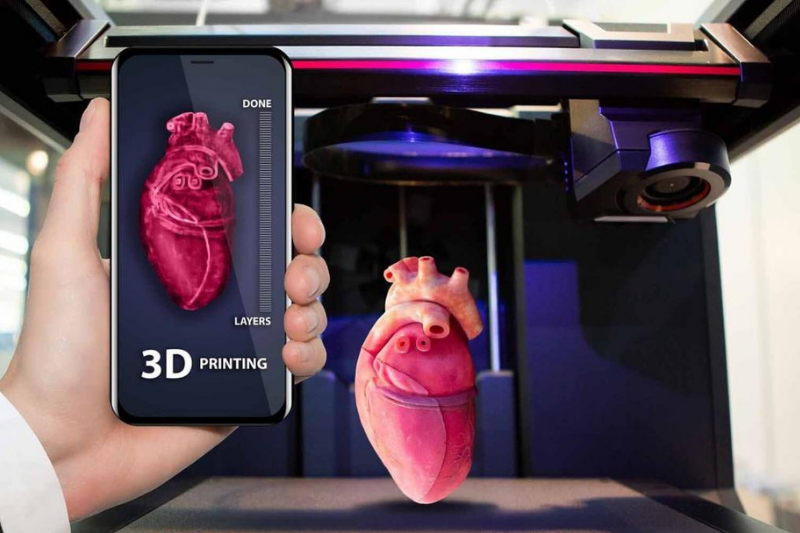

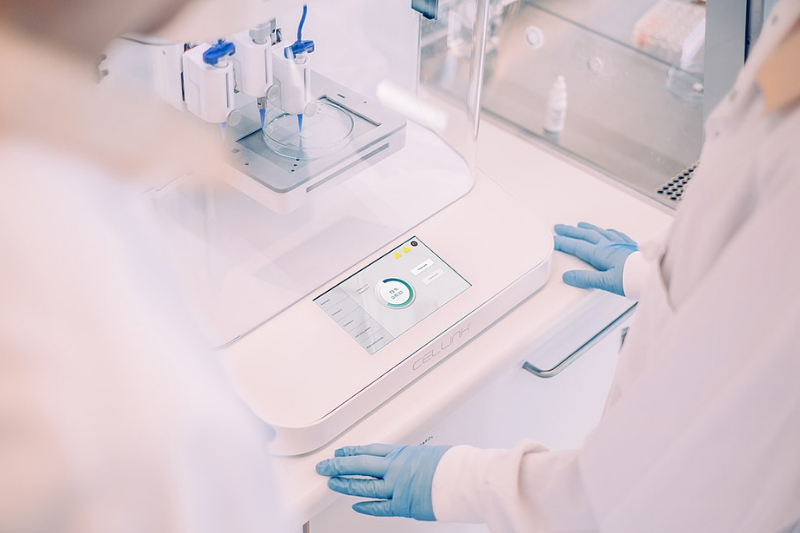
Personalised Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry also hopes to utilise the benefits of 3D printing technology, as it may reduce time for production and delivery. However, the most promising factor of this technology is its capability to produce small quantities of medicine- each with different dosages, shapes, sizes, and release characteristics. This would allow a patient to get the most suitable medication at a personalised level. American pharmaceutical company Aprecia is currently leading research and development (R&D) in this sector.

Food Shortage Solutions
Research is being conducted in Australia to produce food from pureed biomaterials using 3D printers. Other than making food visibly appealing, the applications of this technology could provide solutions to problems of food shortage and dysphagia. With sustainability and world hunger brought to the forefront of global debate, researchers hope to improve the situation through technological advancements in 3D printing.

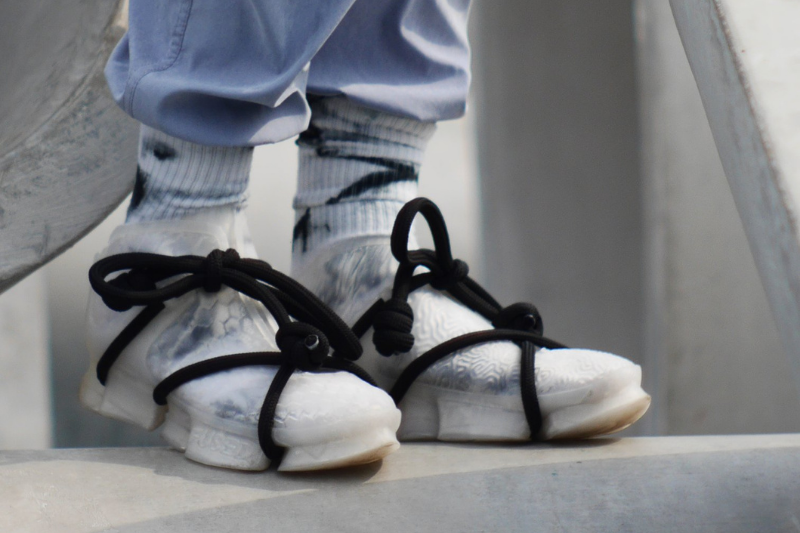
Recyclable Footwear
By using recyclable materials, 3D printing technology is capable of making sustainable products for daily use. FUSED Footwear is a shoe manufacturer based in MakerHive in Hong Kong that uses thermoplastic elastomer as its raw material to produce sneakers using 3D printers. Founded by Philippe Holthuizen with the vision of utilising 3D printing technology to produce aesthetic sustainable footwear, FUSED offers a 20% discount on any new pair for customers who return their old mono-material sneakers.

Barriers to Technological Advancements
As cutting-edge as this technology seems, 3D printing still has a long way to go before becoming mainstream. One major restraint is high material cost. This is a difficult problem for manufacturers to solve because costs are due to the higher standards of purity and composition required for 3D printing.
There are also legal barriers to 3D printing. Although the technology itself may not seem problematic legally speaking, inappropriate use of 3D printing may offend a person’s intellectual property. Moreover, several governments are against the mass utilisation and distribution of 3D printers as they have the potential to create firearms and other weapons.
With 3D printing technology expected to become an influential tech trend in the future, resolutions including appropriate regulations should be prioritised in order for it to further develop.
Featured banner image credit: news-medical.net
Related Articles
Could 3D Printing Be the Future of Architecture? Singaporean Startup AIRLAB Says Yes.